Diagnose A P0420 Check Engine Code on a ODB2 Car
A P0420 ODB2 check engine code or "Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold? code means that the your car has detected a problem related to the efficiency of your catalytic converter. Diagnosing a P0420 engine code is fairly straight forward once you understand how your car's exhaust and emissions systems interact.
Plain English
Your car has a catalytic converter in the exhaust system to control emissions. There are 2 heated oxygen sensors that measure unburnt fuel ratio in the exhaust. One is before the cat, and one after.
The computer monitors the output of these sensors, expecting the front sensor to fluctuate more then the other. If these sensors report similar readings, the catalytic converter may be damaged or not correctly controlling emissions.
Possible Causes
- Leaded fuel used when unleaded is recommended
- A broken or disconnected oxygen (o2) sensor
- A broken or disconnected engine coolant temperature sensor
- exhaust manifold leaks
- Worn or damaged catalytic converter
- exhaust piping leaks
- Retarded/Improper spark timing
- Leaking fuel injector
- High fuel pressure
- Cylinder misfire
- Oil contamination
- Scan Tool
- Hammer
- Infrared Thermometer
- Check Engine Light is on
- Reduced Power
- Rotten egg smell from exhaust
Check for Other Engine Codes
If there are other engine codes present before the p0420 code such as a cylinder misfire, address those first.
Determine Which Catalytic Converter to Inspect
The P0420 code is usually accompanied with "Bank 1" or "Bank 2" which indicates which catalytic converter is causing the code. Bank 1 means the catalytic converter connected to cylinder #1.
For inline 4 cylinder engines common on most passenger cars, there is only one bank.
Vehicles with v6 or v8 engines have 2 banks of cylinders. In this case you may see bank 2 indicating the catalytic converter of concern is on a the 2nd bank of cylinders.
Check for Exhaust Leaks
Leaks in the exhaust before the catalytic converter can cause unexpected oxygen sensor readings. Listen and inspect for exhaust leaks near the exhaust manifold and piping leading up to the catalytic converter.
Inspect Oxygen Sensors
The O2 sensors on each end of the catalytic converter should be checked for wear or damage. Be sure that the wiring is intact and securely plugged into it's wiring harness.
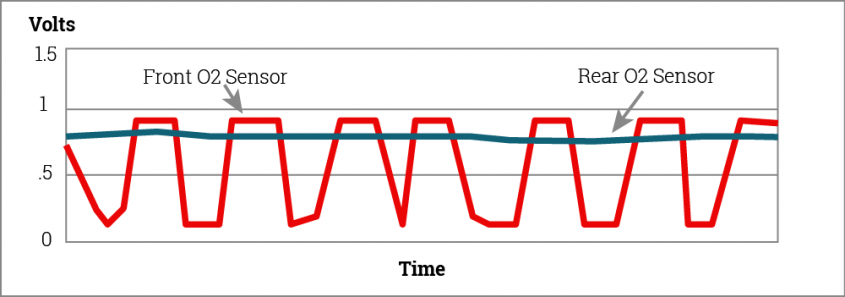
The voltage of each sensor should be compared to verify the expected signals appear. The O2 sensor in front of the cat should fluctuate in voltage while the one to the rear should be more steady.
Use a scan tool, multimeter, or oscilloscope to monitor the voltage from the sensors and compare them against the expected values.
Typical Scan tool labels for the O2 sensors:
- Front Oxygen Sensor: O2S11
- Rear Oxygen Sensor: O2S12
The graph shown depicts what a correctly functioning O2S11 and O2S12 sensor should look like.
Inspect Catalytic Converter
The catalytic converter converts unburnt fuel into less harmful gases using a honeycomb like structure of metal that reacts with the exhaust as it passes through.
Like any other filter, as it ages it can get clogged and deteriorate.
Catalytic converters go bad for numerous reasons.
- Too much fuel, oil, or coolant in exhaust.
- Bad ignition tuning.
- Ignored check engine lights.
- Physical Damage.
- Overheating.
Lightly tap a hammer (not hard enough to dent or dislodge the catalyst material) and listen for loose pieces inside.
Check the temperature of the piping welds before and after the catalyst material using a infrared thermometer.
- Front: 300-500 degrees F
- Rear: Front temperature + 100-150 degrees F
If the rear is considerably hotter, there is too much fuel in the exhaust and the catalyst is working too hard, which will eventually cause it to fail. If the rear is lower then expected, it is likely that the catalytic convert is clogged or damaged.


There are 0 Comments.
Say Something.You have to log in to comment...
We'll publish your comment after you're logged in.
Written by:iturgeon
Related HowTune Articles
Written by:eyewitnessdashcams
Selecting the Dashboard Camera
Written by:iturgeon
Rebuilding a 700R4 Transmission
Written by:iturgeon
Not Getting Ripped off by a Mechanic
Written by:sytyguy
Restore the Plastic Headlight Lenses
Written by:ijdmtoy
Install a Quick Bumper Release
Get notified about new articles.
We don't sell or share your info.